Fistula or fistula (from lat. fistula - tube) - a channel that connects between itself or the external environment hollow organs or a tumor with the surface or any body cavity. It usually has the form of a narrow channel lined with epithelium.
Fistulas are divided into those that formed as a result of any pathological process in the body, and those that formed after a surgical operation performed to remove the contents from any hollow organ.
Fistula - reasons
Causes of purulent fistula:
-After closing the focus of inflammation, the pus should go outside, the channel through which it flows usually subsequently painlessly heals. But in cases where the process of inflammation is not completely eliminated, a cavity with an infection continues to be located in the depth of the tissues, sometimes even with a sequester (a dead part of the bone), the canal does not grow together, and a purulent fistula forms.
- In chronic periodontitis, fistulas can occur from the roots of the tooth, passing through the jaw and gum.
-after blind gunshot wounds, if during the time fragments and a bullet were not removed from the body, then suppuration forms next to them.
- fistulas are formed during suppuration of sutures near the ligatures (a thread used to ligate blood vessels)
Fistula - Symptoms
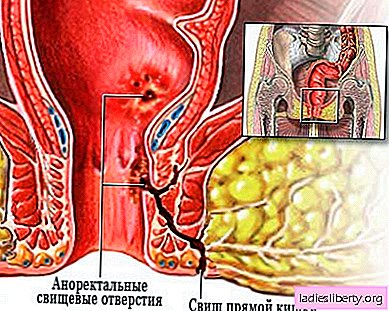
Symptoms of a fistula of the rectum:
-the presence of a small hole in the anus. Often there is abundant discharge of pus, so patients have to wear a pad and take a shower several times a day.
aching pain in the anus. Usually they are the strongest during bowel movements, after which they gradually subside.
Symptoms of bronchial fistula:
-perfection of the technique of suturing the stump of the bronchi.
-specific endobronchitis.
Symptoms of a fistula on the gum:
- toothache intensifying when touched.
- tooth mobility.
purulent discharge from the channel of the fistula.
Fistula - Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the fistula does not create particular difficulties. It is based on the characteristic complaints of patients, the anamnesis, the number and composition of pus secreted, the form of fistula, with interorgan fistulas on a change in the functions performed by these organs.
To clarify the direction of the fistulous passage, its length, as well as the connection with the pathological focus, etc. usually used. sounding, radiography along with the introduction of contrast agents into the fistula.
They help to clarify the diagnosis of the study for the presence of hydrochloric acid, this can convince that the fistula is located in the stomach. The presence of uric acid salts is usually characteristic of a urinary fistula and so on.
Fistula - treatment and prevention
Mainly treat fistulas surgically. Many purulent fistulas formed after the operation can be eliminated in a simple way - by removing the ligatures using a hemostatic clamp.
In addition to eliminating the inflammatory focus itself, it is necessary to completely remove the epithelial cover of the passage of the fistula.
Congenital fistulas are fought immediately and surgically, since without external intervention the child dies for the first time in his life. In most cases, the independent closure of purulent canals of the fistula is almost impossible. Lip-shaped fistulas are treated only with radical operations that involve mobilizing the walls of the genital organ and suturing its openings.
Prevention, most often acquired fistula, includes various kinds of prevention of infectious diseases. It is also necessary to strictly observe the rules of asepsis during surgical interventions.
Prevention of congenital fistula is not treatable, because this disease occurs around the first trimester of pregnancy.











